Guillain-Barré Syndrome: Understanding the Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
GBS can cause a wide range of symptoms, from numbness and tingling in the hands and feet to paralysis of the entire body. In some cases, GBS can even be fatal.
There is currently no cure for GBS, but treatment can help to improve symptoms and speed up recovery.
| Condition | Symptoms | Treatment |
| Guillain-Barré Syndrome | Weakness and numbness in the legs, arms, and face; difficulty breathing; and paralysis | Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) or plasmapheresis |
| Transverse Myelitis | Weakness and numbness in the legs and arms; difficulty with bowel and bladder function | Steroids and other medications |
| Multiple Sclerosis | Numbness and tingling in the hands and feet; vision problems; and fatigue | Medications to modify the immune system |

Guillain-Barré Syndrome: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment - Premier - Source premierneurologycenter.com
FAQ
Frequently asked questions and expert answers about Guillain-Barré Syndrome.

Understanding Cold Sweats: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment options - Source www.world-today-news.com
Question 1: What is Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS)?
GBS is an autoimmune disorder in which the body's immune system attacks its own nervous system. This can lead to weakness, numbness, and tingling in the legs, arms, chest, or face.
Question 2: What are the symptoms of GBS?
Symptoms of GBS can vary, but typically start with weakness and numbness in the legs. As the disease progresses, the weakness and numbness can spread to the arms, chest, and face. Other symptoms may include difficulty breathing, swallowing, and speaking.
Question 3: What causes GBS?
The exact cause of GBS is unknown, but it is thought to be triggered by an infection, such as a recent bout of gastroenteritis, Epstein-Barr virus, or the flu. The immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own nervous system, leading to the symptoms of GBS.
Question 4: How is GBS diagnosed?
GBS is diagnosed based on a physical examination and a nerve conduction study. A nerve conduction study measures the electrical activity of the nerves and can help to confirm the diagnosis of GBS.
Question 5: How is GBS treated?
There is no cure for GBS, but treatment can help to improve symptoms and speed up recovery. Treatment typically involves intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) or plasmapheresis. Both treatments work by removing the antibodies that are attacking the nervous system.
Question 6: What is the prognosis for GBS?
The prognosis for GBS varies. About 60-80% of people make a full recovery within a few months. However, some people may experience long-term problems, such as weakness, fatigue, or numbness.
For more information on GBS, please consult a healthcare professional.
For the latest information on the ever evolving symptoms of Long Covid, browse our library of articles.
Tips for Understanding Guillain-Barré Syndrome
Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) is a rare neurological disorder that affects the peripheral nervous system, which is responsible for sending signals between the brain and the rest of the body. GBS can cause a variety of symptoms, including muscle weakness, numbness, and tingling. In severe cases, GBS can lead to paralysis and death.
There is no cure for GBS, but treatment can help to improve symptoms and prevent complications. Treatment options include intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), plasmapheresis, and physical therapy. Guillain-Barré Syndrome: Understanding The Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment Options provide detailed guidance on the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for GBS.
Tip 1: Learn about the symptoms of GBS.
The symptoms of GBS can vary from person to person. Some of the most common symptoms include:
- Muscle weakness
- Numbness and tingling
- Difficulty breathing
- Difficulty swallowing
- Double vision
- Speech problems
Tip 2: Know the risk factors for GBS.
The exact cause of GBS is unknown, but it is thought to be triggered by an infection. Some of the risk factors for GBS include:
- Recent surgery
- Recent infection, such as the flu or a stomach bug
- Certain autoimmune disorders
Tip 3: Seek medical attention if you experience symptoms of GBS.
If you experience any of the symptoms of GBS, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. Early diagnosis and treatment can help to improve outcomes.
Tip 4: Follow your doctor's instructions carefully.
If you are diagnosed with GBS, it is important to follow your doctor's instructions carefully. This may include taking medication, undergoing physical therapy, and making lifestyle changes.
Tip 5: Be patient and positive.
Recovery from GBS can take time and effort. It is important to be patient and positive during this process. With the right treatment and support, most people with GBS are able to make a full recovery.
For more detailed information and support, please refer to Guillain-Barré Syndrome: Understanding The Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment Options.
Guillain-Barré Syndrome: Understanding The Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment Options
Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) is an immune-mediated neurological disorder that affects the peripheral nervous system. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for effective management. Here are six key aspects to explore:
- Causes: Infection, immune disorders, surgery
- Symptoms: Weakness, numbness, tingling, difficulty breathing
- Diagnosis: Physical exam, nerve conduction studies, lumbar puncture
- Treatment: Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), plasmapheresis
- Recovery: Time frame varies, rehabilitation may be needed
- Prognosis: Majority improve, but some may experience long-term effects

Sanai Spotlights Meningioma Symptoms, Treatment Options, and Research Needs - Source www.onclive.com
GBS triggers an autoimmune response, where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its own nervous system. Symptoms typically develop over days to weeks, and vary in severity. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are essential, as GBS can progress rapidly and lead to significant complications. Recovery can take months or even years, and may involve physical and occupational therapy. Despite advancements in treatment, GBS remains a complex and challenging condition, highlighting the need for continued research and support for patients and their families.
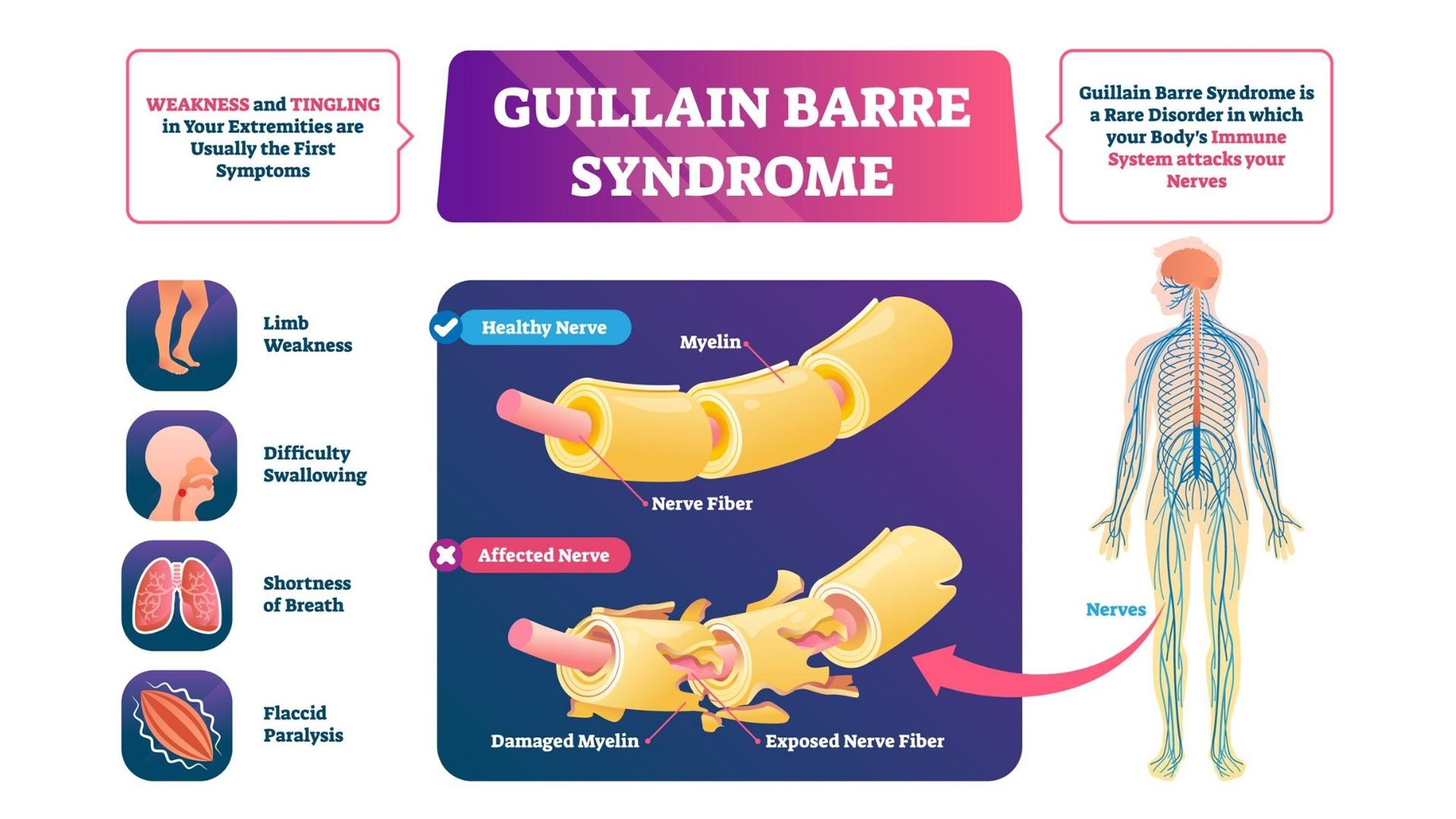
Guillain-Barré syndrome | Causes | Symptoms | Types | Treatment, and - Source yourneurodoctor.in
Guillain-Barré Syndrome: Understanding The Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment Options
Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) is a rare autoimmune disorder that affects the peripheral nervous system. It is characterized by rapidly progressive muscle weakness, which can lead to paralysis in severe cases. The exact cause of GBS is unknown, but it is thought to be triggered by an infection, such as a recent bout of gastroenteritis or Epstein-Barr virus.

Tennis Elbow vs. Golfer’s Elbow: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment - Source www.flagstaffbusinessnews.com
GBS can affect people of all ages, but it is most common in adults between the ages of 30 and 50. The symptoms of GBS can vary depending on the severity of the condition, but they typically include:
- Muscle weakness in the legs and arms
- Numbness and tingling in the hands and feet
- Difficulty breathing
- Double vision
- Difficulty swallowing
There is no cure for GBS, but the symptoms can be treated. Treatment options include:
- Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG)
- Plasmapheresis
- Physical therapy
- Occupational therapy
The prognosis for GBS varies depending on the severity of the condition. In most cases, the symptoms improve within a few weeks or months. However, some people may experience long-term effects, such as muscle weakness and fatigue.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Cause | Unknown, but thought to be triggered by an infection |
| Symptoms | Muscle weakness, numbness and tingling, difficulty breathing, double vision, difficulty swallowing |
| Treatment | Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), plasmapheresis, physical therapy, occupational therapy |
| Prognosis | Varies depending on severity; most people recover within a few weeks or months |