Foot And Mouth Disease: Causes, Symptoms, And Prevention
Editor's Notes: Foot And Mouth Disease: Causes, Symptoms, And Prevention have published today date.
We realize that Foot And Mouth Disease: Causes, Symptoms, And Prevention is a complex topic. That's why we spent numerous long hours doing some analysis, digging through piles of information, and putting together this Foot And Mouth Disease: Causes, Symptoms, And Prevention guide to help you make the right decision.
Key differences or Key takeways:
Transition to main article topics:

Hand foot and mouth disease hfmd – Artofit - Source www.artofit.org
FAQ
This FAQ section aims to provide comprehensive information about foot and mouth disease, addressing common concerns and misconceptions.

Hand Foot And Mouth Disease Symptoms Adult - Source mungfali.com
Question 1: What are the primary causes of foot and mouth disease?
Foot and mouth disease is primarily caused by infection with the foot and mouth disease virus. The virus is highly contagious and can spread through direct contact with infected animals or their secretions, as well as through contaminated food, water, and equipment.
Question 2: What are the common symptoms of foot and mouth disease?
The symptoms of foot and mouth disease can vary in severity but typically include fever, blisters or ulcers in the mouth, on the tongue, and on the feet and teats, lameness, reduced appetite, and excessive salivation.
Question 3: How is foot and mouth disease diagnosed?
Foot and mouth disease is diagnosed based on clinical symptoms and laboratory testing. Samples of blood, saliva, or blisters can be tested to confirm the presence of the virus.
Question 4: What are the preventive measures for foot and mouth disease?
Effective preventive measures for foot and mouth disease include vaccination of livestock, practicing good hygiene and biosecurity measures, avoiding contact with infected animals, and promptly reporting any suspected cases to veterinary authorities.
Question 5: How is foot and mouth disease treated?
There is no specific cure for foot and mouth disease. Treatment focuses on supportive care, such as providing pain relief, preventing dehydration, and maintaining nutrition. Antibiotics may be used to prevent or treat secondary bacterial infections.
Question 6: What are the potential economic impacts of foot and mouth disease?
Foot and mouth disease can have significant economic impacts, leading to trade restrictions, loss of livestock, decreased production, and disruption of agricultural markets.
By understanding these key aspects of foot and mouth disease, individuals can contribute to effective prevention and control measures.
Moving beyond these FAQs, the next section delves into the transmission and spread of foot and mouth disease, exploring the means by which the virus disseminates and infects susceptible hosts.
Tips
Foot and mouth disease is Foot And Mouth Disease: Causes, Symptoms, And Prevention highly contagious among livestock, causing severe economic losses. Here are critical tips to prevent and control the disease:
Tip 1: Restrict Animal Movements
Avoid transporting animals from infected areas. Restrict movement between farms and limit access to livestock markets.
Tip 2: Biosecurity Measures
Implement strict biosecurity protocols at farms, including disinfection of vehicles, equipment, and clothing. Quarantine new animals and isolate any showing symptoms.
Tip 3: Vaccination
Vaccinate susceptible animals annually or as directed by local regulations. Vaccination can help prevent infection or reduce the severity of symptoms.
Tip 4: Surveillance and Reporting
Regularly monitor livestock for signs of illness. Report any suspected cases to veterinary authorities promptly. Early detection and reporting are crucial for effective disease control.
Tip 5: Control of Vectors
Manage vector populations, such as flies and rodents, to prevent the spread of the disease. Keep animal sheds clean and free of manure and garbage.
Summary of key takeaways or benefits
By implementing these tips, farmers can significantly reduce the risk of foot and mouth disease outbreaks, protect their livestock, and safeguard public health.
Transition to the article's conclusion
Foot and mouth disease control requires collaboration among farmers, veterinarians, and government agencies. Adhering to these preventive measures is essential to minimize the impact of this devastating disease on livestock production and global food security.
Foot And Mouth Disease: Causes, Symptoms, And Prevention
Foot and mouth disease (FMD) is a highly contagious viral disease of cloven-hoofed animals. It causes significant economic losses due to reduced productivity, trade restrictions, and animal welfare concerns.
- Etiology: FMD virus, a picornavirus.
- Transmission: Contact with infected animals, their saliva, or contaminated objects.
- Symptoms: Fever, blisters in the mouth and feet, lameness.
- Diagnosis: Clinical signs, laboratory testing.
- Prevention: Vaccination, biosecurity measures (quarantine, disinfection), movement control.
- Control: Stamping out infected animals, vaccination campaigns, surveillance.
Successful control and prevention of FMD rely on early detection, stringent biosecurity practices, and effective vaccination programs. International collaboration and cooperation are crucial for preventing its spread across borders and minimizing its impact on global animal agriculture and food security.
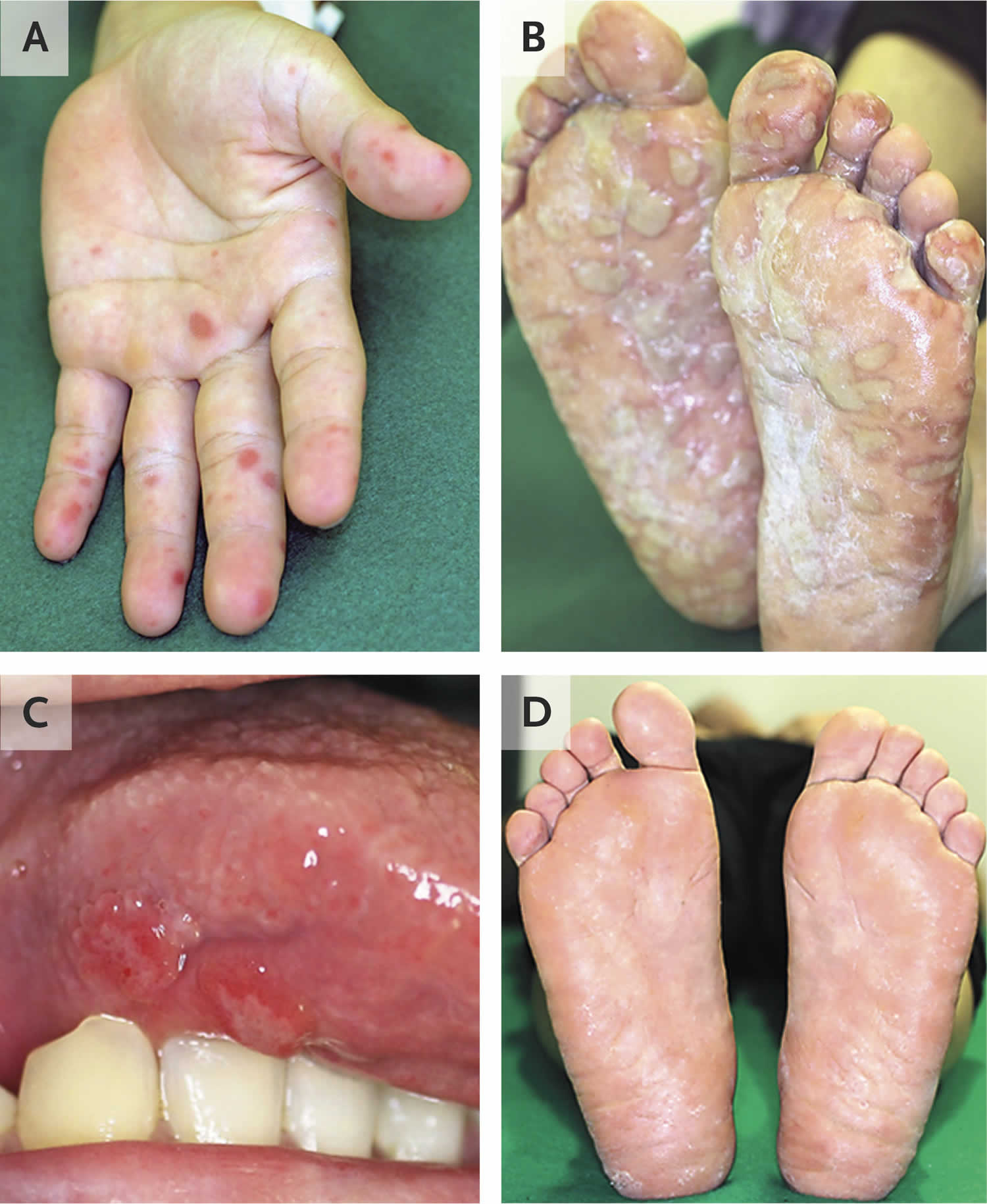
Hand Foot And Mouth Disease Causes Signs Symptoms Diagnosis | Images - Source www.aiophotoz.com
Hand, foot and mouth disease. Causes, symptoms, treatment Hand, foot - Source www.dxline.info
Foot And Mouth Disease: Causes, Symptoms, And Prevention
Foot and mouth disease (FMD) is a highly contagious viral disease that affects cloven-hoofed animals, including cattle, swine, sheep, goats, and deer. The virus is spread through contact with infected animals or their saliva, mucus, or feces. FMD can cause severe economic losses due to its impact on animal health and production.

Hand Foot Mouth Disease Symptoms - Discover 10 common hand foot and - Source jditast.blogspot.com
The causes of FMD are complex and involve a variety of factors, including the type of virus, the host animal, and the environment. The virus is highly transmissible and can be spread through close contact between infected and susceptible animals, as well as through contaminated food, water, or equipment. The symptoms of FMD can vary depending on the strain of the virus and the species of animal infected.
Prevention of FMD is essential to protect animal health and the economy. Measures include vaccination, quarantine, and movement restrictions. Vaccination is the most effective method of preventing FMD, and it is recommended for all cloven-hoofed animals in areas where the disease is present or has the potential to occur. Quarantine and movement restrictions can help to prevent the spread of the disease by limiting the contact between infected and susceptible animals.
FMD is a serious disease that can have a significant impact on animal health and production. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and prevention of FMD is essential for protecting animals and the economy.
| Cause | Symptom | Prevention |
|---|---|---|
| Virus | Fever, blisters, lameness | Vaccination, quarantine, movement restrictions |
Conclusion
FMD is a complex and challenging disease, but it can be prevented and controlled through effective vaccination programs, quarantine and movement restrictions, and other biosecurity measures. By working together, we can protect our animals and our economy from the devastating effects of FMD.
The fight against FMD is not over, but we have made significant progress. By continuing to work together, we can achieve our goal of a world free from FMD.
