Editor's Note: "Understanding the Differences Between CTC and WWW for Effective Website Optimization" article has been published today. This topic is important to read because it provides insights into the technical aspects of website optimization.
Our team has analyzed and dug into a wealth of information, resulting in this comprehensive guide on "Understanding the Differences Between CTC and WWW for Effective Website Optimization." This guide will help you make informed decisions.
Key Differences:
| Feature | CTC | WWW |
|---|---|---|
| Protocol | Content Transfer Content | World Wide Web |
| Purpose | Email and FTP | Web Browsing |
| Security | Encrypted | Unencrypted |
FAQ
Unveiling the complexities of website optimization, this FAQ section aims to clarify the distinctions between CTC and WWW, providing insights into their impact on effective website performance and search engine visibility.
Question 1: What is the primary difference between CTC and WWW when optimizing a website?
CTC (Content Type Content) refers to the actual content of a web page, encompassing text, images, videos, and other elements that convey information to users. On the other hand, WWW (World Wide Web) represents the platform or infrastructure that enables the accessibility and interconnectivity of websites across the internet.
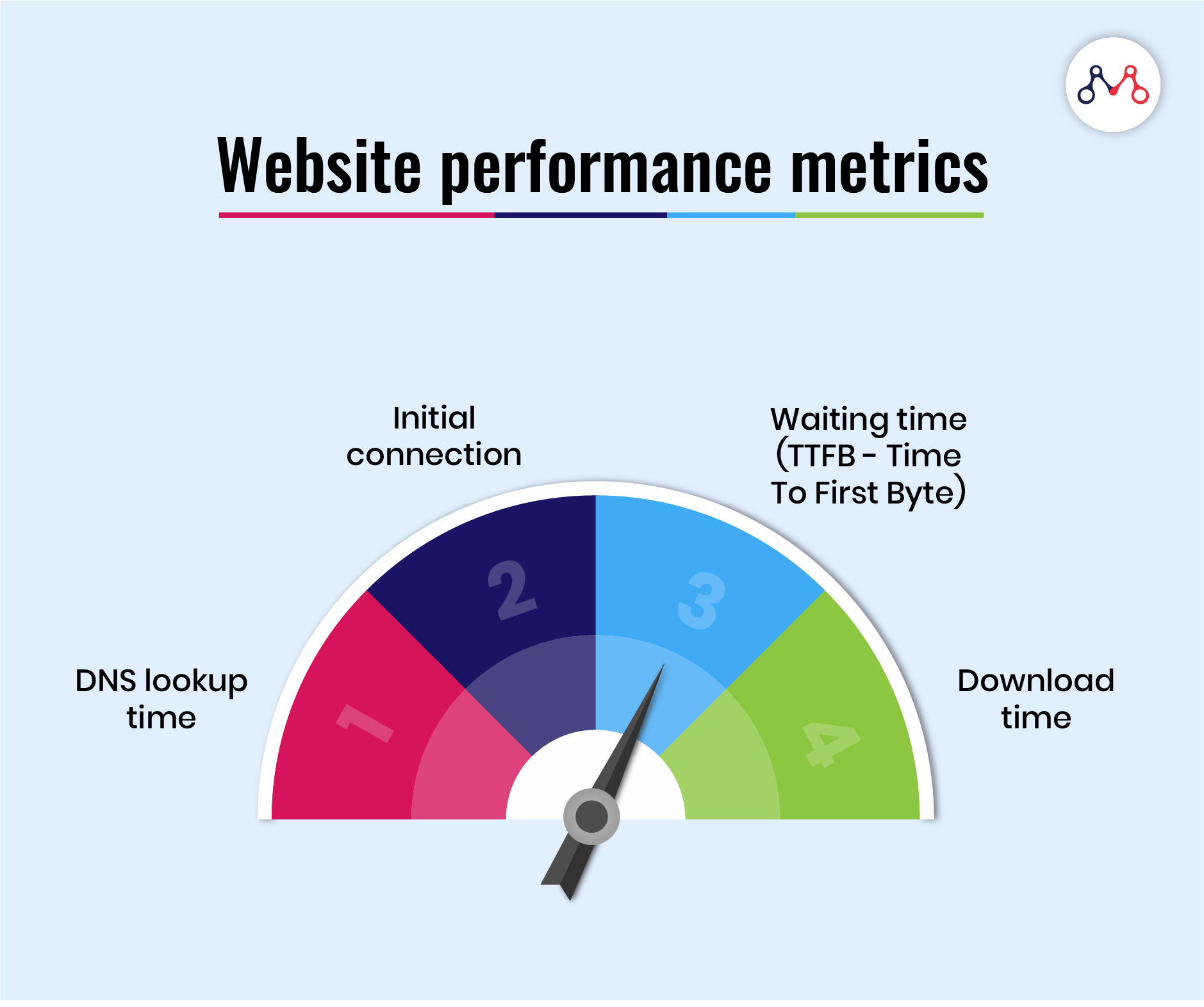
Website Performance Optimization Techniques 2025 - Uta M. Mueller - Source utammueller.pages.dev
Question 2: How does CTC influence website optimization?
CTC plays a pivotal role in website optimization by providing search engines with valuable information about the page's relevance and authority. Well-optimized CTC improves a website's ranking in search results by demonstrating its alignment with specific keywords and user queries.
Question 3: What aspects of WWW are relevant to optimization?
WWW optimization focuses on ensuring that websites are accessible and visible to search engines. It encompasses technical factors such as site structure, page load speed, mobile responsiveness, and adherence to web standards. By optimizing these elements, websites can improve their visibility and user experience.
Question 4: How can optimizing both CTC and WWW enhance website performance?
Optimizing both CTC and WWW synergistically improves website performance by ensuring that relevant content is presented in a technically sound environment. This combination enhances the user experience, increases engagement, and ultimately leads to improved search engine rankings.
Question 5: What are some common pitfalls to avoid when optimizing CTC and WWW?
Common pitfalls include keyword stuffing, creating low-quality backlinks, neglecting technical SEO, and ignoring user experience. By avoiding these mistakes and adhering to best practices, websites can effectively achieve their optimization goals.
Question 6: How can businesses stay updated on the latest trends and best practices for CTC and WWW optimization?
To stay abreast of the latest trends and best practices, businesses should regularly consult reliable sources of information, attend industry events, and seek professional guidance from experienced SEO specialists.
In conclusion, understanding the nuances between CTC and WWW is paramount for effective website optimization. By focusing on both content quality and technical soundness, websites can enhance their visibility, improve user engagement, and achieve their desired outcomes.
To delve deeper into the topic of website optimization, explore our next article section, "Essential Elements of Website Optimization: A Comprehensive Guide.
Tips
Optimizing a website for search engines is vital for its visibility and success online. Two crucial aspects to consider in website optimization are the correct usage of CTC (Content Type-type) and WWW (World Wide Web). Understanding The Differences Between CTC And WWW For Effective Website Optimization helps ensure that search engines can crawl and index a website efficiently, leading to improved search rankings and increased organic traffic.
Tip 1: Choose the Right CTC
CTC specifies the format of the content on a webpage, such as HTML, XML, or JSON. Search engines prefer HTML as it is widely supported and easily parsed. Using the correct CTC helps search engines understand the content type, making it easier for them to categorize and index the webpage.
Tip 2: Use WWW for Consistency
The WWW subdomain is a common practice in website addresses. It indicates that the website is accessible via the internet, making it easier for users to remember and access. Using WWW consistently throughout the website, including internal links and external references, ensures that search engines can easily track and index all pages.
Tip 3: Avoid Duplicate Content
Having multiple versions of the same content with different CTCs or WWW/non-WWW URLs can lead to duplicate content issues. This can confuse search engines and result in lower rankings. Use canonical tags or 301 redirects to consolidate duplicate content and ensure that search engines prioritize the preferred version.
Tip 4: Implement Structured Data
Structured data provides search engines with additional information about the content on a webpage, making it easier to understand and index. Use schema markup to highlight important elements such as articles, products, or events, helping search engines display rich snippets and improve search visibility.
Tip 5: Monitor and Adjust
Website optimization is an ongoing process that requires regular monitoring and adjustments. Use analytics tools to track website traffic, search rankings, and user behavior. Based on the data, make necessary changes to the CTC, WWW usage, and content to continually improve website performance and search engine optimization.
In conclusion, understanding the differences between CTC and WWW and implementing them correctly is essential for effective website optimization. By following these tips, website owners can ensure that their websites are easily crawlable, indexable, and visible in search engine results, leading to increased organic traffic and improved online presence.
Understanding The Differences Between CTC And WWW For Effective Website Optimization
Optimizing a website for search engines involves understanding the difference between CTC and WWW. Website optimization can be affected by the type of URL used, which can be either CTC or WWW.
- CTC: No WWW prefix, implying a secure connection.
- WWW: Includes WWW prefix, indicating a non-secure connection.
- Ranking: Search engines treat CTC and WWW URLs differently for ranking purposes.
- Protocol: CTC URLs use HTTPS protocol, while WWW URLs use HTTP protocol.
- Security: CTC URLs provide a more secure connection, encrypting data transmitted between the website and the visitor's browser.
- User Perception: WWW URLs may be perceived as less secure, potentially affecting user trust.
Choosing between CTC and WWW depends on the specific website's requirements and security considerations. For websites handling sensitive information, CTC URLs are recommended. However, for websites where security is less critical, WWW URLs may be sufficient. Understanding these differences is crucial for effective website optimization and ensuring the best user experience.

Strategies for Website Optimization - Transformation Marketing - Source www.transformationmarketing.com
Understanding The Differences Between CTC And WWW For Effective Website Optimization
Understanding the difference between CTC (canonical tag) and WWW (www-prefix) is crucial for effective website optimization. A canonical tag specifies the preferred version of a webpage, while a www-prefix is the subdomain used to access a website. Using both correctly ensures search engines index the desired version and avoid duplicate content issues.
Islamic State military organizational chart, undated – Combating - Source ctc.westpoint.edu
CTCs are crucial for websites with multiple versions of the same page, such as with and without www. By specifying the preferred version, search engines can avoid indexing both versions, which can lead to lower rankings and lost traffic. WWW-prefixes, on the other hand, are often used for historical reasons or to differentiate websites from their non-www versions.
Properly implementing CTCs and WWW-prefixes requires careful consideration. CTCs should be placed in the
section of the HTML code, while WWW-prefixes should be consistent across all internal and external links. Failure to use them correctly can result in search engine penalties or indexing issues.Understanding the differences between CTCs and WWWs is essential for website owners and SEOs. By implementing them correctly, they can ensure search engines index the desired version of their website, avoid duplicate content issues, and improve overall website performance.
| Feature | CTC (Canonical Tag) | WWW (www-Prefix) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Specifies the preferred version of a webpage | Subdomain used to access a website |
| Location | section of HTML code | Subdomain in the URL |
| Importance for SEO | Prevents duplicate content issues | Historical and branding reasons |
| Impact on website performance | Improved search engine rankings and traffic | Can affect website consistency and branding |
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between CTCs and WWW is crucial for effective website optimization. CTCs prevent duplicate content issues and improve search engine rankings, while WWW-prefixes maintain website consistency and branding. By implementing both correctly, website owners and SEOs can ensure search engines index the desired version of their website and improve overall website performance.
Going forward, it is important to stay updated on search engine guidelines and best practices regarding CTCs and WWWs. By leveraging this knowledge, website owners can ensure their websites are optimized for search engines and deliver the best possible user experience.